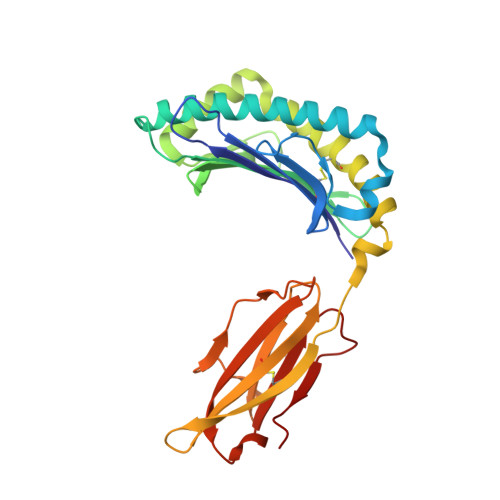
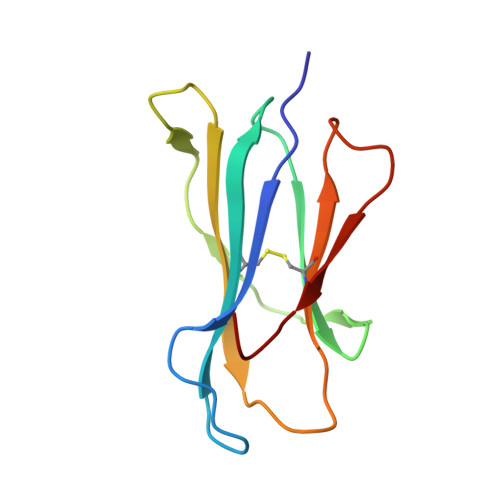
Crystal structures of H-2Db in complex with the LCMV-derived peptides GP92 and GP392 explain pleiotropic effects of glycosylation on antigen presentation and immunogenicity.
Hafstrand, I., Badia-Martinez, D., Josey, B.J., Norstrom, M., Buratto, J., Pellegrino, S., Duru, A.D., Sandalova, T., Achour, A.(2017) PLoS One 12: e0189584-e0189584
- PubMed: 29253009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0189584
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5JWD, 5JWE - PubMed Abstract:
Post-translational modifications significantly broaden the epitope repertoire for major histocompatibility class I complexes (MHC-I) and may allow viruses to escape immune recognition. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection of H-2b mice generates CD8+ CTL responses directed towards several MHC-I-restricted epitopes including the peptides GP92 (CSANNSHHYI) and GP392 (WLVTNGSYL), both with a N-glycosylation site. Interestingly, glycosylation has different effects on the immunogenicity and association capacity of these two epitopes to H-2Db. To assess the structural bases underlying these functional results, we determined the crystal structures of H-2Db in complex with GP92 (CSANNSHHYI) and GP392 (WLVTNGSYL) to 2.4 and 2.5 Å resolution, respectively. The structures reveal that while glycosylation of GP392 most probably impairs binding, the glycosylation of the asparagine residue in GP92, which protrudes towards the solvent, possibly allows for immune escape and/or forms a neo-epitope that may select for a different set of CD8 T cells. Altogether, the presented results provide a structural platform underlying the effects of post-translational modifications on epitope binding and/or immunogenicity, resulting in viral immune escape.
- Science for Life Laboratory, Department of Medicine Solna, Karolinska Institutet, and Department of Infectious Diseases, Karolinska University Hospital, Solna, Stockholm, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: