Discovery of novel covalent selective estrogen receptor degraders against endocrine-resistant breast cancer.
Wang, Y., Min, J., Deng, X., Feng, T., Hu, H., Guo, X., Cheng, Y., Xie, B., Yang, Y., Chen, C.C., Guo, R.T., Dong, C., Zhou, H.B.(2023) Acta Pharm Sin B 13: 4963-4982
- PubMed: 38045063
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2023.05.005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7YMK - PubMed Abstract:
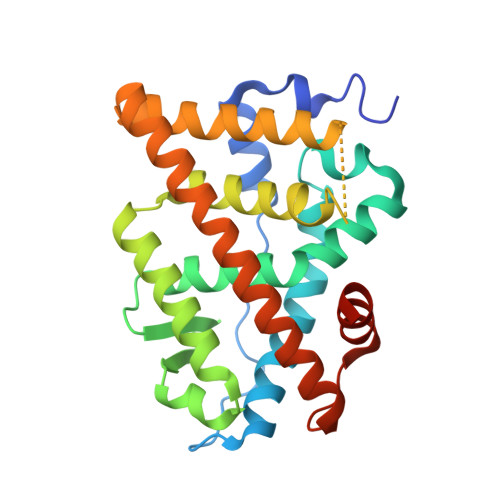
Endocrine-resistance remains a major challenge in estrogen receptor α positive (ER α + ) breast cancer (BC) treatment and constitutively active somatic mutations in ER α are a common mechanism. There is an urgent need to develop novel drugs with new mode of mechanism to fight endocrine-resistance. Given aberrant ER α activity, we herein report the identification of novel covalent selective estrogen receptor degraders (cSERDs) possessing the advantages of both covalent and degradation strategies. A highly potent cSERD 29c was identified with superior anti-proliferative activity than fulvestrant against a panel of ER α + breast cancer cell lines including mutant ER α . Crystal structure of ER α ‒ 29c complex alongside intact mass spectrometry revealed that 29c disrupted ER α protein homeostasis through covalent targeting C530 and strong hydrophobic interaction collied on H11, thus enforcing a unique antagonist conformation and driving the ER α degradation. These significant effects of the cSERD on ER α homeostasis, unlike typical ER α degraders that occur directly via long side chains perturbing the morphology of H12, demonstrating a distinct mechanism of action (MoA). In vivo , 29c showed potent antitumor activity in MCF-7 tumor xenograft models and low toxicity. This proof-of-principle study verifies that novel cSERDs offering new opportunities for the development of innovative therapies for endocrine-resistant BC.
- Department of Gynecological Oncology, Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Wuhan University, Wuhan 430071, China.
Organizational Affiliation: