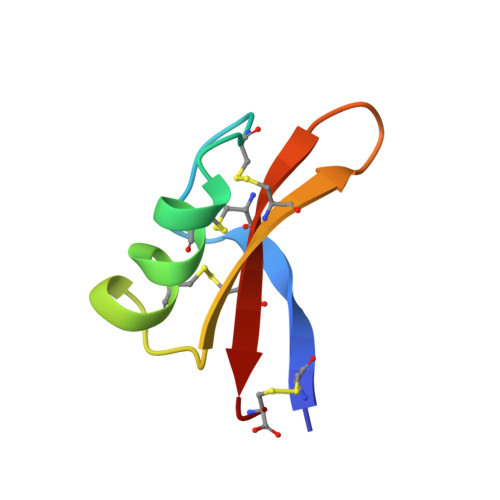
The three-dimensional solution structure of Aesculus hippocastanum antimicrobial protein 1 determined by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance.
Fant, F., Vranken, W.F., Borremans, F.A.(1999) Proteins 37: 388-403
- PubMed: 10591099
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0134(19991115)37:3<388::aid-prot7>3.3.co;2-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1BK8 - PubMed Abstract:
Aesculus hippocastanum antimicrobial protein 1 (Ah-AMP1) is a plant defensin isolated from horse chestnuts. The plant defensins have been divided in several subfamilies according to their amino acid sequence homology. Ah-AMP1, belonging to subfamily A2, inhibits growth of a broad range of fungi. So far, a three-dimensional structure has been determined only for members of subfamilies A3 and B2. In order to understand activity and specificity of these plant defensins, the structure of a protein belonging to subfamily A2 is needed. We report the three-dimensional solution structure of Ah-AMP1 as determined from two-dimensional 1H nuclear magnetic resonance data. The structure features all the characteristics of the "cysteine-stabilized alpha beta-motif." A comparison of the structure, the electrostatic potential surface and regions important for interaction with the fungal receptor, is made with Rs-AFP1 (plant defensin of subfamily A3). Thus, residues important for activity and specificity have been assigned.
- Department of Organic Chemistry, University of Gent, Belgium. franky.fant@rug.ac.be
Organizational Affiliation: