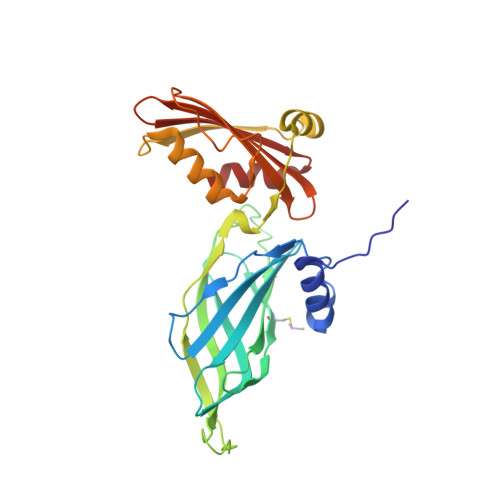
Gamma-COP appendage domain - structure and function
Watson, P.J., Frigerio, G., Collins, B.M., Duden, R., Owen, D.J.(2004) Traffic 5: 79-88
- PubMed: 14690497
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-0854.2004.00158.x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1R4X - PubMed Abstract:
COPI-coated vesicles mediate retrograde transport from the Golgi back to the ER and intra-Golgi transport. The cytosolic precursor of the COPI coat, the heptameric coatomer complex, can be thought of as composed of two subcomplexes. The first consists of the beta-, gamma-, delta- and zeta-COP subunits which are distantly homologous to AP clathrin adaptor subunits. The second consists of the alpha-, beta'- and epsilon-COP subunits. Here, we present the structure of the appendage domain of gamma-COP and show that it has a similar overall fold as the alpha-appendage of AP2. Again, like the alpha-appendage the gamma-COP appendage possesses a single protein/protein interaction site on its platform subdomain. We show that in yeast this site binds to the ARFGAP Glo3p, and in mammalian gamma-COP this site binds to a Glo3p orthologue, ARFGAP2. On the basis of mutations in the yeast homologue of gamma-COP, Sec21p, a second binding site is proposed to exist on the gamma-COP appendage that interacts with the alpha,beta',epsilon COPI subcomplex.
- Cambridge Institute for Medical Research & Department of Clinical Biochemistry, University of Cambridge, Hills Road, Cambridge CB2 2XY, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: