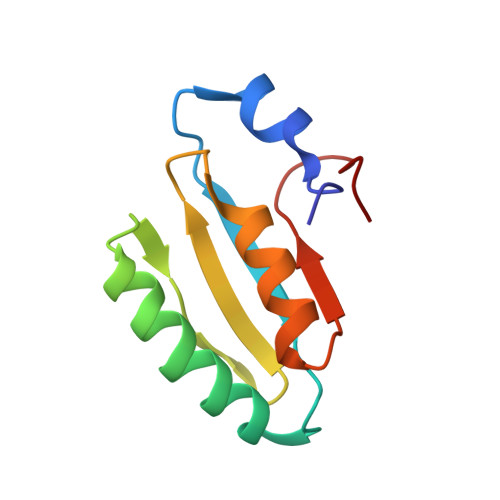
The solution structure of the core of mesoderm development (MESD), a chaperone for members of the LDLR-family
Kohler, C., Andersen, O.M., Diehl, A., Krause, G., Schmieder, P., Oschkinat, H.(2006) J Struct Funct Genomics 7: 131-138
- PubMed: 17342452
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10969-007-9016-5
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2I9S - PubMed Abstract:
Mesoderm development (MESD) is a 224 amino acid mouse protein that acts as a molecular chaperone for receptors of the low-density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) family. By recording (15)N-HSQC-NMR spectra of six different MESD constructs, we could determine a highly structured core region corresponding to residues 104-177. Here we firstly present the solution structure of this highly conserved core of MESD. It shows a four-stranded anti-parallel beta-sheet and two alpha-helices situated on one side of the sheet. Although described in the literature as structurally homologues to ferredoxins, the connectivity of secondary structure elements is different in the MESD fold. A structural comparison to entries of the PDB reveals a frequent domain with low sequence homology annotated as HMA and P-II domains in Pfam.
- Department of NMR-Supported Structural Biology, Leibniz-Institut für Molekulare Pharmakologie, Robert-Rössle-Str. 10, 13125 Berlin, Germany.
Organizational Affiliation: