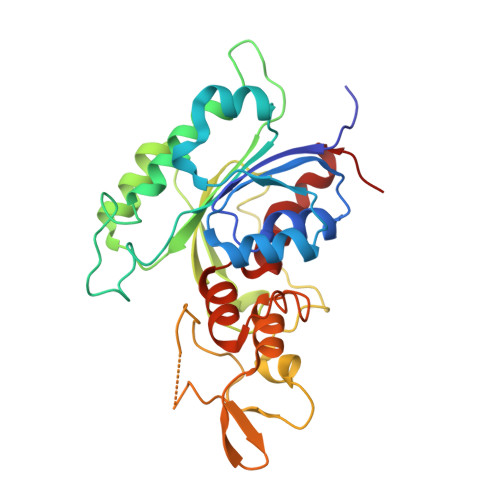
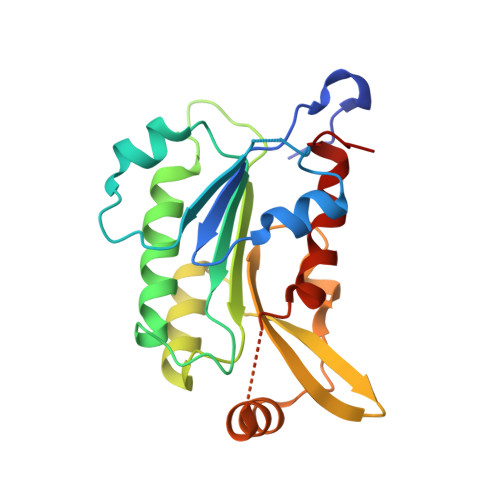
Mechanistic Insights into Harmine-Mediated Inhibition of Human DNA Methyltransferases and Prostate Cancer Cell Growth.
Cho, C.C., Lin, C.J., Huang, H.H., Yang, W.Z., Fei, C.Y., Lin, H.Y., Lee, M.S., Yuan, H.S.(2023) ACS Chem Biol 18: 1335-1350
- PubMed: 37188336
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.3c00065
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7X9D - PubMed Abstract:
Mammalian DNA methyltransferases (DNMTs), including DNMT1, DNMT3A, and DNMT3B, are key DNA methylation enzymes and play important roles in gene expression regulation. Dysregulation of DNMTs is linked to various diseases and carcinogenesis, and therefore except for the two approved anticancer azanucleoside drugs, various non-nucleoside DNMT inhibitors have been identified and reported. However, the underlying mechanisms for the inhibitory activity of these non-nucleoside inhibitors still remain largely unknown. Here, we systematically tested and compared the inhibition activities of five non-nucleoside inhibitors toward the three human DNMTs. We found that harmine and nanaomycin A blocked the methyltransferase activity of DNMT3A and DNMT3B more efficiently than resveratrol, EGCG, and RG108. We further determined the crystal structure of harmine in complex with the catalytic domain of the DNMT3B-DNMT3L tetramer revealing that harmine binds at the adenine cavity of the SAM-binding pocket in DNMT3B. Our kinetics assays confirm that harmine competes with SAM to competitively inhibit DNMT3B-3L activity with a K i of 6.6 μM. Cell-based studies further show that harmine treatment inhibits castration-resistant prostate cancer cell (CRPC) proliferation with an IC 50 of ∼14 μM. The CPRC cells treated with harmine resulted in reactivating silenced hypermethylated genes compared to the untreated cells, and harmine cooperated with an androgen antagonist, bicalutamide, to effectively inhibit the proliferation of CRPC cells. Our study thus reveals, for the first time, the inhibitory mechanism of harmine on DNMTs and highlights new strategies for developing novel DNMT inhibitors for cancer treatment.
- Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan 11529, Republic of China.
Organizational Affiliation: