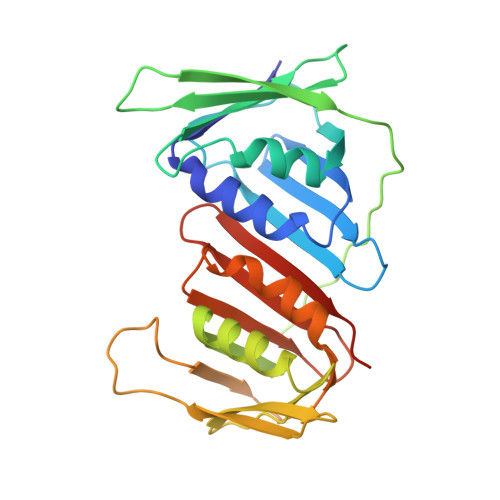
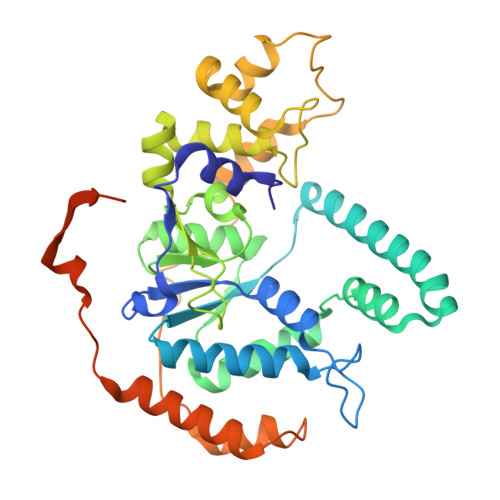
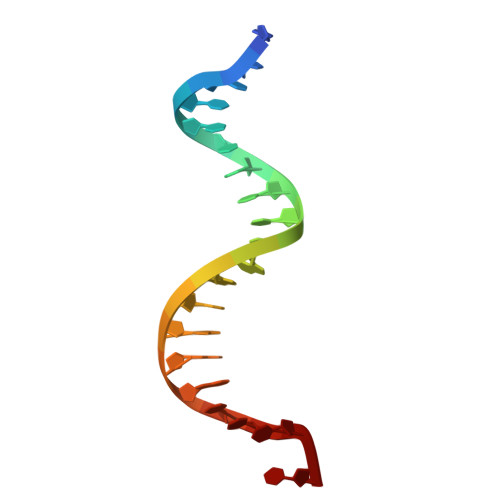
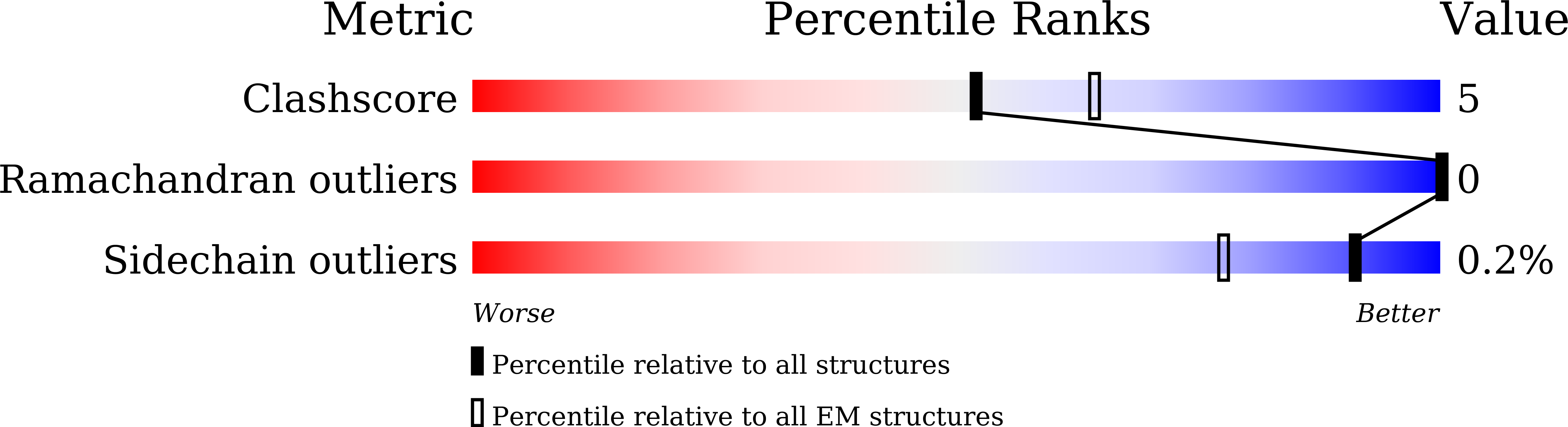Structural insight into Okazaki fragment maturation mediated by PCNA-bound FEN1 and RNaseH2.
Tian, Y., Li, N., Li, Q., Gao, N.(2024) EMBO J
- PubMed: 39578540
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44318-024-00296-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8YJH, 8YJL, 8YJQ, 8YJR, 8YJS, 8YJU, 8YJV, 8YJW, 8YJZ - PubMed Abstract:
PCNA is a master coordinator of many DNA-metabolic events. During DNA replication, the maturation of Okazaki fragments involves at least four DNA enzymes, all of which contain PCNA-interacting motifs. However, the temporal relationships and functional modulations between these PCNA-binding proteins are unclear. Here, we developed a strategy to purify endogenous PCNA-containing complexes from native chromatin, and characterized their structures using cryo-EM. Two structurally resolved classes (PCNA-FEN1 and PCNA-FEN1-RNaseH2 complexes) have captured a series of 3D snapshots for the primer-removal steps of Okazaki fragment maturation. These structures show that product release from FEN1 is a rate-liming step. Furthermore, both FEN1 and RNaseH2 undergo continuous conformational changes on PCNA that result in constant fluctuations in the bending angle of substrate DNA at the nick site, implying that these enzymes could regulate each other through conformational modulation of the bound DNA. The structures of the PCNA-FEN1-RNaseH2 complex confirm the toolbelt function of PCNA and suggests a potential unrecognized role of RNaseH2, as a dsDNA binding protein, in promoting the 5'-flap cleaving activity of FEN1.
Organizational Affiliation:
State Key Laboratory of Membrane Biology, Peking-Tsinghua Joint Center for Life Sciences, School of Life Sciences, Peking University, Beijing, China.