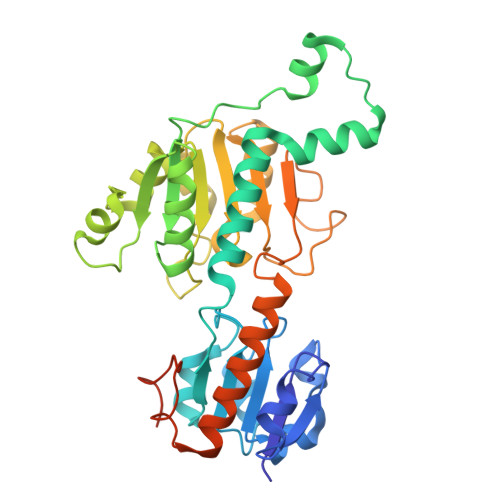
PALI1 enhances CtBP1/2 oligomerization and couples CtBP1/2 to PRC2.
Zhang, B., Jiang, J., Chen, P., Lin, C., Sun, W., Wang, J., Li, W., Chen, J., Luo, Q., Cai, D., Cai, Q., Chen, S.(2026) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 800: 153295-153295
- PubMed: 41547303
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2026.153295
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9WRJ - PubMed Abstract:
Polycomb Repressive Complex 2 (PRC2) and C-terminal binding proteins 1 and 2 (CtBP1/2) are key epigenetic regulators that frequently co-occupy chromatin, yet their crosstalk remains poorly understood. Here, we delineate the molecular basis of the interaction between CtBP1/2 and the N-terminal domain of PALI1, an accessory subunit of PRC2. The PALI1 N-terminus contains two DLS-like motifs that bind CtBP1/2 bivalently, enhancing affinity and promoting higher-order oligomerization. Conversely, disruption of CtBP1/2 oligomerization weakens PALI1 binding, revealing a reciprocal mechanism stabilizing the CtBP1/2-PALI1 complex. The 2.20 Å structure of the CtBP1-PALI1 complex reveals the detailed interaction interface, which, together with biochemical data, supports a model where tandem DLS-like motifs drive CtBP1/2 oligomerization and multivalent engagement. Through its C-terminal PRC2-binding domain, PALI1 acts as a dual-interface scaffold linking CtBP1/2 and PRC2, providing a structural framework for their coordinated chromatin recruitment and transcriptional repression.
- School of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Innovative Drug Target Research, Xiamen University, Xiamen, 361102, China.
Organizational Affiliation: