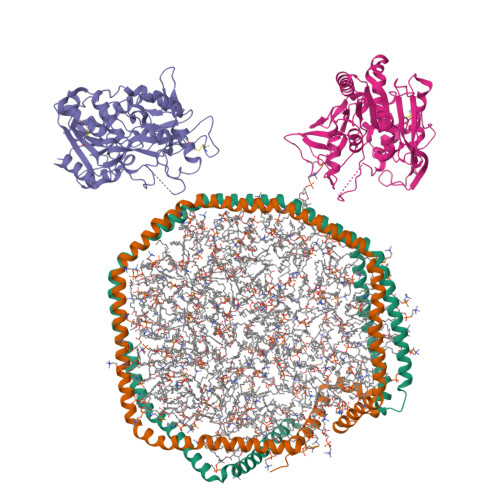
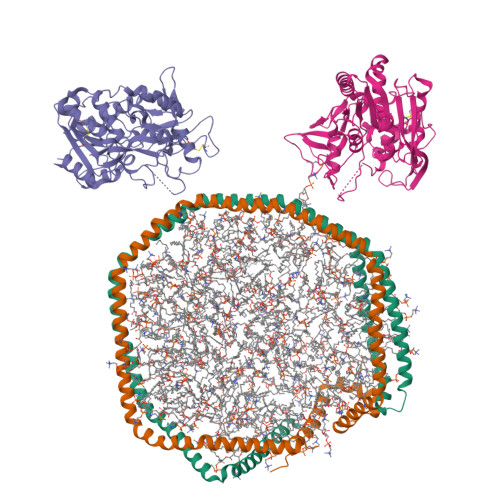
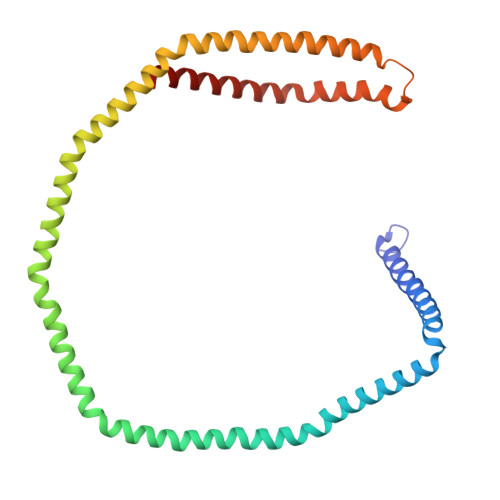
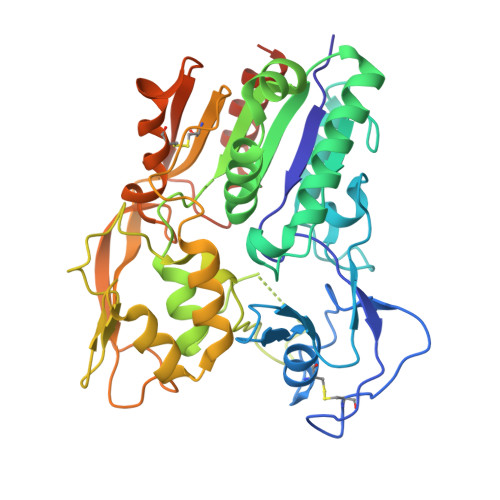
Lecithin:Cholesterol Acyltransferase Binds a Discontinuous Binding Site on Adjacent Apolipoprotein A-I Belts in HDL.
Coleman, B., Bedi, S., Hill, J.H., Morris, J., Manthei, K.A., Hart, R.C., He, Y., Shah, A.S., Jerome, W.G., Vaisar, T., Bornfeldt, K.E., Song, H., Segrest, J.P., Heinecke, J.W., Aller, S.G., Tesmer, J.J.G., Davidson, W.S.(2025) J Lipid Res : 100786-100786
- PubMed: 40147634
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlr.2025.100786
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9MXZ - PubMed Abstract:
Lecithin:cholesterol acyltransferase (LCAT) is a high-density lipoprotein (HDL) modifying protein that profoundly affects the composition and function of HDL subspecies. The cholesterol esterification activity of LCAT is dramatically increased by apolipoprotein A-I (APOA1) on HDL, but the mechanism remains unclear. Using site-directed mutagenesis, cross-linking, mass spectrometry, electron microscopy, protein engineering and molecular docking, we identified two LCAT binding sites formed by helices 4 and 6 from two antiparallel APOA1 molecules in HDL. Although the reciprocating APOA1 'belts' form two ostensibly symmetrical binding locations, LCAT can adopt distinct orientations at each site, as shown by our 9.8 Å cryoEM envelope. In one case, LCAT membrane binding domains align with the APOA1 belts and, in the other, the HDL phospholipids. By introducing disulfide bonds between the APOA1 helical domains, we demonstrated that LCAT does not require helical separation during its reaction cycle. This indicates that LCAT, anchored to APOA1 belts, accesses substrates and deposits products through interactions with the planar lipid surface. This model of the LCAT/APOA1 interaction provides insights into how LCAT and possibly other HDL-modifying factors engage the APOA1 scaffold, offering potential strategies to enhance LCAT activity in individuals with genetic defects.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Molecular and Cellular Biosciences, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, USA.